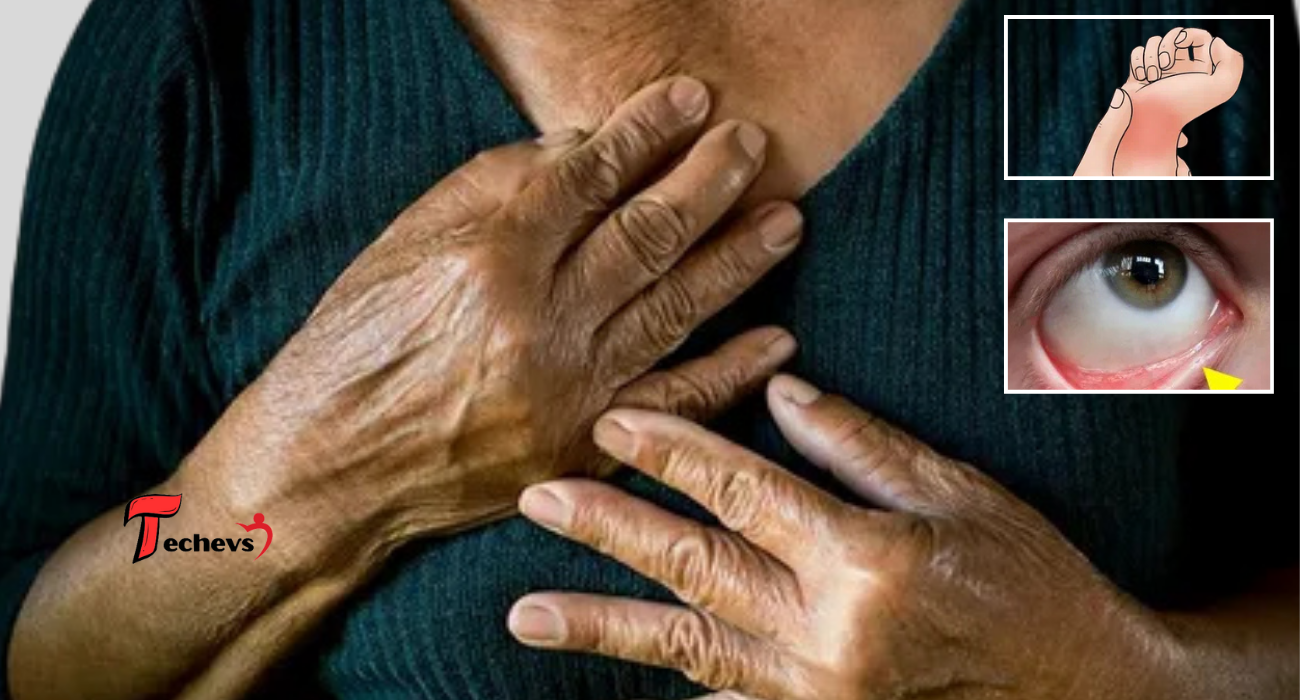
What do genetic mutations do?
Gene mutations can cause healthy cells to:
Promote rapid growth:
Mutations can cause cells to grow and divide more quickly, resulting in more cells containing the same mutation.
Prevent abnormal growth:
Cancer cells lose the control mechanisms (tumor suppressor genes) that normally signal cells to grow. Mutations in these genes lead to uncontrolled growth.
Make DNA repair errors:
DNA repair genes are responsible for correcting mistakes in a cell’s DNA. When these genes mutate, the mistakes are not corrected, resulting in cancerous cells.